

Code: PRO1191
Heatsinks for medium power
| Lega | BxS Dimensione | Peso al metro |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | [[part1]] | [[part2]] |
| Codice | KN MAX | I | F | H |
|---|
| Codice | KN MAX | I | F | H |
|---|
| Codice | KN MAX | I | F | H |
|---|
| Codice | KN MAX | I | F | H |
|---|
| Codice | KN MAX | I | F | H |
|---|
| Codice | KN MAX | I | F | H |
|---|
Length: 200.00 mm
Weight: 3.90 kg/m
Weight A: 0.00 kg/m
Weight B: 0.00 kg/m
Height: 15.00 mm
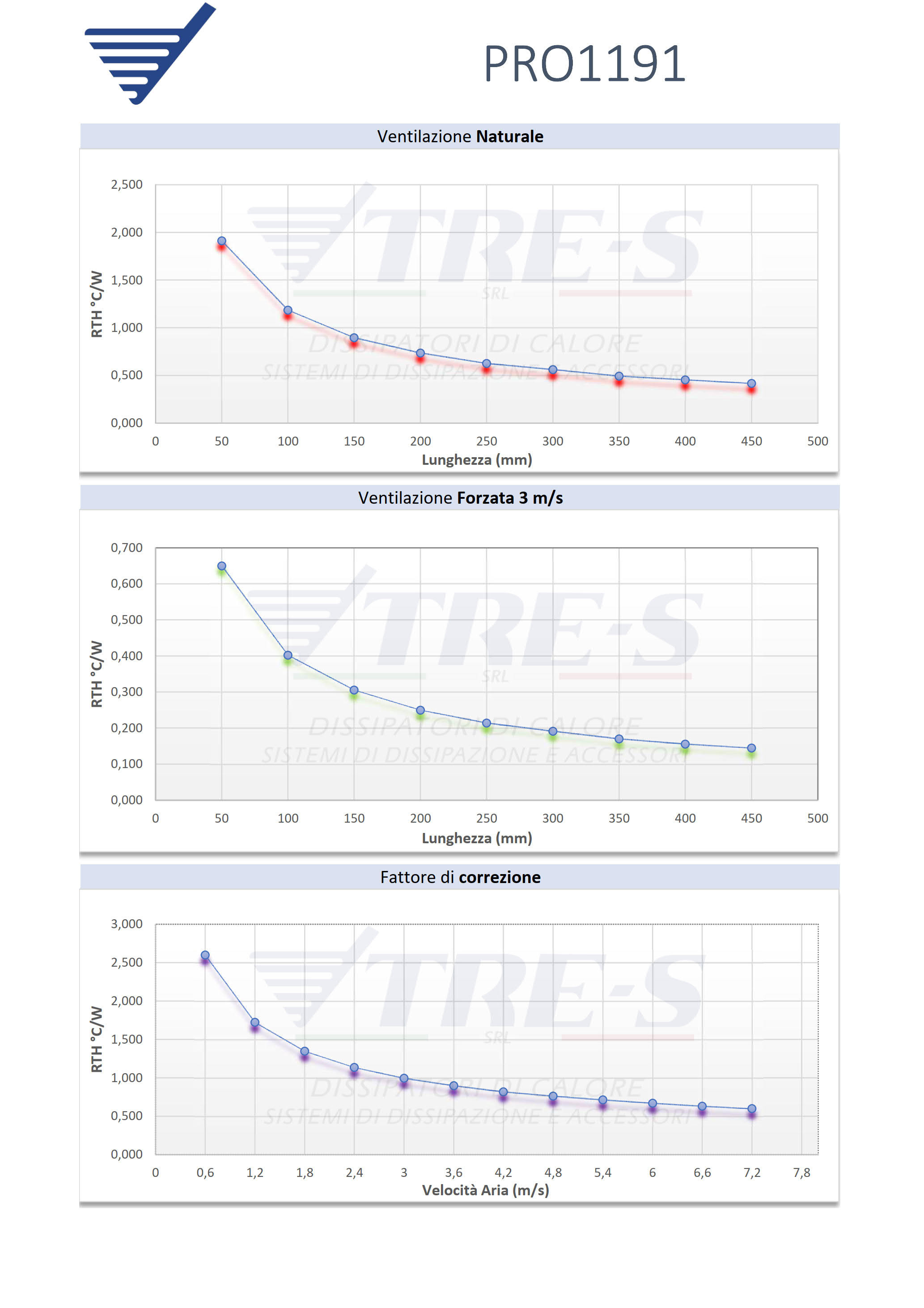
Within this catalog, heat sinks are organized based on their shape and dimensions expressed in millimeters. Each profile is characterized by the following parameters:
- Weight: expressed in kilograms per meter of profile length (Kg/m).
- Length: indicated in millimeters and used for calculating thermal resistance (L).
- Width: also in millimeters, considered for calculating thermal resistance (°C/W), applicable only to high-efficiency heat sinks.
- Thermal Resistance in Natural Convection: expressed in °C/W with a temperature difference of 70°C (compared to an ambient temperature of 25°C).
- Thermal Resistance in Forced Convection: also expressed in °C/W, with an air velocity of 3 m/s and a temperature difference of 50°C.
The values of thermal resistance have been determined through a thermal simulation program designed to replicate realistic conditions. In particular:
- The heat source is uniformly distributed over approximately 50% of the dissipation surface, with central positioning on the heat sink.
- To maximize natural convection heat dissipation efficiency, the heat sink is designed with vertical fins. For horizontal installations, it is advisable to consider an increase of approximately 20% in thermal resistance.
- The surface of the heat sink is not subject to additional treatments.
Regarding black anodized heat sinks in natural convection, the thermal resistance is reduced by approximately 10%.
As the length of the heat sink increases, the thermal resistance decreases following a nonlinear law. The indicated values refer to the specified lengths; for different lengths, consult the “Length Correction Factor” graph to calculate the multiplication factor to be applied to the thermal resistance, both in natural and forced convection.

